What Are Antioxidants?

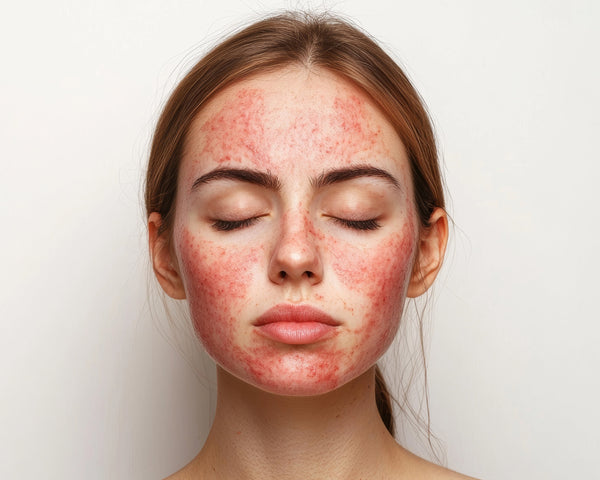
Antioxidants are enzymes that protect the body from the oxidative stress caused by free radicals. Free radicals are compounds that interfere with the cell’s ability to function normally, which in most cases lead to cell damage. They are created in the body during normal metabolic functions and can be introduced by external factors in the environment. However, just as the body produces free radicals, it also produces antioxidants, a means to defend the body against the harmful effects of free radicals.
Studies have uncovered a direct link between free radicals and many health conditions. Some of those conditions include but are not limited to autoimmune disorder, inflammatory disorder, rheumatoid arthritis, and aging (decrease in skin elasticity, wrinkles, gray hair, etc…). Antioxidants combat free radicals by reducing the energy of free radicals, preventing the formation of free radicals, or interrupting the oxidizing reaction to decrease the damage caused free radicals.
The human body produces different types of antioxidants including include superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and catalases. Supplements of these antioxidant enzymes can also available; However, the body does not absorb the supplement form of antioxidant as well. The best way to ensure that the body is getting the antioxidants it needs is to supplement with the building blocks that enable the body to manufacture its own antioxidants. The supplements/building blocks needed to make this possible include manganese, zinc, and copper.
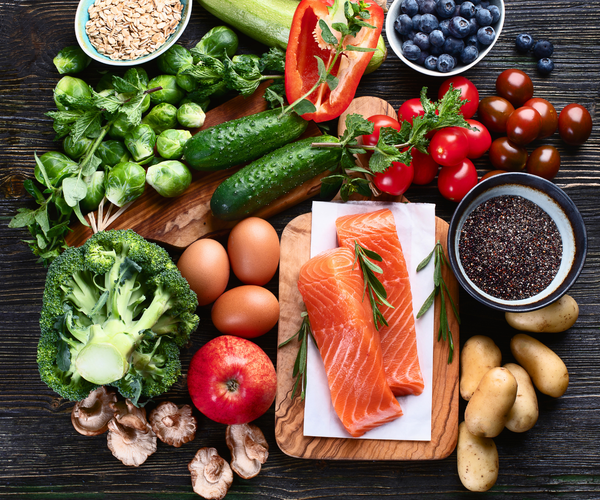
Some plants, including fruits and vegetables, are considered natural antioxidants. The human body cannot produce its own supply of natural antioxidants; that is why we have to depend solely on our diet to get the amount of antioxidants our body needs.
Catechins, coumarins, indoles, and carotenoids are a group of well-known antioxidants. They are the complex compound found in just about every plant. The largest group of natural antioxidants are the carotenoids. The next largest group is the insoles. The antioxidants found in camellia sinuses plants, which is where we get green tea, oolong tea, and black tea, are the catechins.
Many vitamins and nutrients have antioxidant properties. Vitamins C, A (beta carotene), E, and B12 and nutrients coenzyme Q10, cysteine, lycopene, lutein and others are included in the list. Tumeric, ginkgo, pine bark, and a host of other herbs also provide powerful antioxidant protection for the body.