What is Acne-Prone Skin and How to Care for It

What is Acne-Prone Skin?
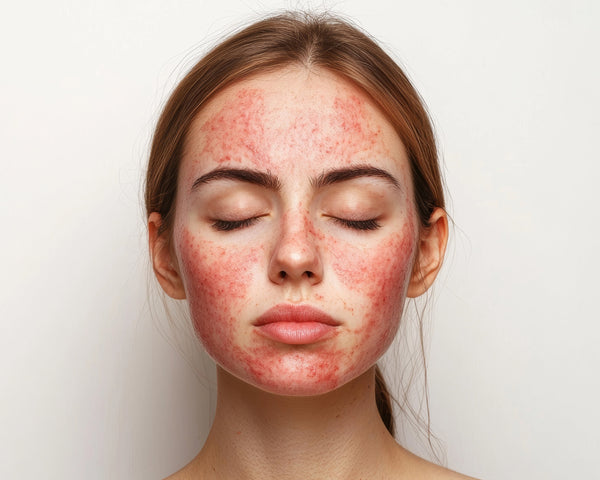
Acne-prone skin is a skin type characterized by a tendency to develop acne breakouts. These breakouts can range from mild blackheads and whiteheads to more severe cystic acne. The condition is caused by a complex interplay of factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, and bacterial overgrowth. Understanding these factors is key to effectively managing acne-prone skin.
Identifying Acne-Prone Skin
Several key indicators can help you determine if you have acne-prone skin:
- Frequent breakouts: Regular appearance of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, or cysts.
- Inflammation: Redness, swelling, and tenderness around breakouts.
- Oily skin: A noticeable shine or greasiness, especially in the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin).
- Enlarged pores: Pores that appear larger than average.
- Clogged pores: A feeling of roughness or texture on the skin.
Causes of Acne-Prone Skin
Acne development is a multi-factorial process. Key contributors include:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, or pregnancy can trigger increased sebum production, leading to clogged pores.
- Genetics: A family history of acne significantly increases your risk.
- Excess sebum production: Sebum, an oily substance produced by sebaceous glands, can clog pores when overproduced.
- Bacteria: Cutibacterium acnes (formerly known as Propionibacterium acnes) is a bacteria that thrives in clogged pores and contributes to inflammation.
- Dead skin cells: The buildup of dead skin cells can clog pores and exacerbate acne.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids and lithium, can induce acne.
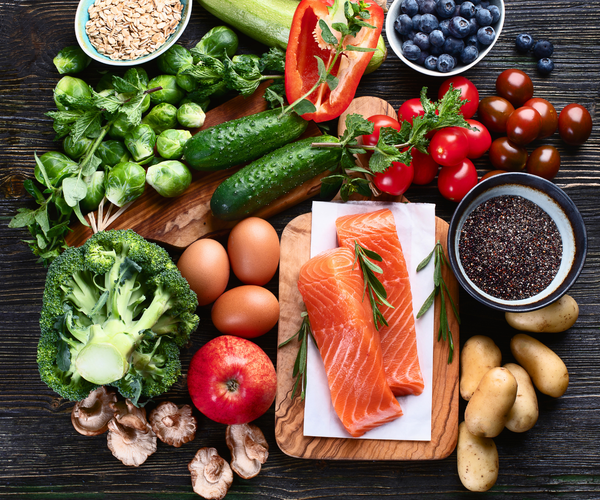
- Diet: While not a direct cause, a diet high in processed foods and refined sugars may worsen acne in some individuals.
- Stress: Stress can trigger hormonal changes that may exacerbate acne.
Caring for Acne-Prone Skin
Effective acne management requires a holistic approach encompassing lifestyle changes and a consistent skincare routine. Here's a detailed guide:
1. Gentle Cleansing:
Wash your face twice daily with a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser. Avoid harsh scrubbing, which can irritate the skin and worsen inflammation.
2. Exfoliation:
Regular exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells and prevent pore clogging. Use a chemical exfoliant containing salicylic acid or glycolic acid 1-2 times per week. Avoid harsh physical scrubs.
3. Topical Treatments:
Over-the-counter topical treatments containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can effectively treat mild to moderate acne. For more severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe stronger medications such as retinoids or antibiotics.
4. Moisturizing:
Even oily skin needs moisture. Choose a lightweight, oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated without clogging pores.
5. Sunscreen:
Always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, even on cloudy days. Some acne treatments can increase sun sensitivity.
6. Diet and Lifestyle:
Maintain a balanced diet, manage stress levels, and get enough sleep. These factors can significantly impact your skin's health.
7. Hands Off!:
Avoid touching your face frequently, as this can transfer bacteria and worsen breakouts.
8. Consult a Dermatologist:
If you have severe acne or if over-the-counter treatments aren't effective, consult a dermatologist. They can provide personalized treatment plans and address any underlying issues.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Will acne scars disappear?
A: Some acne scars fade over time, while others may require professional treatment, such as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser therapy.
Q: Can I use makeup if I have acne-prone skin?
A: Yes, but choose non-comedogenic, oil-free makeup and remove it thoroughly at the end of the day.
Q: How long does it take to see results from acne treatments?
A: It varies depending on the severity of your acne and the treatment used. You may see improvement within a few weeks, but consistent use is crucial for long-term results.
Conclusion
Managing acne-prone skin requires patience and persistence. By following a consistent skincare routine and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can significantly reduce breakouts and improve your skin's overall health. Remember to consult a dermatologist if you have concerns or experience persistent acne.